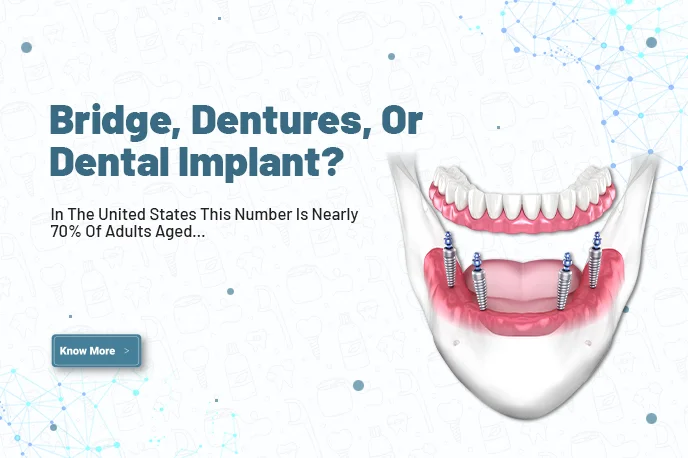
It is estimated that 70% of adults between 35 and 44 years old have lost at least one adult tooth, and by the age of 74, a quarter of Americans have lost all of their adult teeth.
After losing a tooth, it is necessary to get a replacement to keep the rest of your teeth aligned. It also helps to maintain your facial shape to provide a perfect and long-lasting smile and to avoid difficulties while eating or speaking.
In this blog, we will discuss which dental prosthesis is the best treatment for replacing missing or lost teeth based on your situation and overall health condition.
Which To Choose Dental Implants Vs. Bridges & Dentures
Different types of Dentures, bridges, and dental implants are the three most reliable treatment options for a lost or missing tooth.
But to immediately answer the question of which treatment is better, then dental implants are the best tooth replacement method, without question.
The bottom line is that dental implants replace the lost tooth root in the jaw, which prevents bone loss, tooth movement, gum disease, and further tooth loss from occurring in the future.
Prosthetics like dental bridges replace the tooth aesthetically and cause unnecessary damage to otherwise healthy teeth in the process, offering patients a short-term solution instead of a long-term fixed option.
Factors To Consider To Choose The Best Dental Treatment
Making an appointment with a dentist can advise you on the best tooth replacement for your missing or lost tooth, depending on your situation.
Your dentist will recommend dental treatment based on these conditions to determine the best option for you.
-
Number of missing teeth
If you have missing teeth that are more than one consecutive tooth, a dental bridge is likely to be a better option than dental implants.
For each missing tooth, a separate implant needs to be surgically attached to your jawbone, leading to expensive and often impractical surgery.
-
Overall health
Dental prosthesis requires surgery, so they may not be an option for people who have any existing medical conditions that can slow down their healing, such as (diabetes or leukemia).
The best candidates for dental prosthesis are people with great overall health and have a jawbone free of decay that is healthy enough to support the implant.
-
Time
The entire process of getting a cosmetic dental treatment can take months, while a dental bridge can be easily installed in two trips to your dentist and spread over a couple of weeks.
When getting cosmetic dental treatment, an oral surgeon drills a hole to attach the root of an implant to the bone.
Then, they will insert a temporary denture while you wait for the bone to heal. You’ll then have to wait at least from 2 to 6 months.
-
Cost
If you have dental insurance, it is likely to cover a dental bridge than a dental implant.
If you don’t have insurance and both options are out of your budget, then your dentist may recommend you to have a partial denture.
Difference Between Bridges, Dentures, And Dental Implants
You must know the differences, advantages, and disadvantages to find the best option according to your situation.
-
Dental Implants
It is one of the most popular dental treatments and the ideal solution performed by dental professionals or surgeons for replacing missing or lost teeth.
A dental implant is a metallic structure used to replace a missing tooth and to fill the gap between teeth caused by the missing tooth.
With screw-like devices, the surgeon inserts and transplants into the jawbone, which acts as an anchor for an artificial tooth called a crown.
Implants are generally manufactured from Titanium, a metal that is compatible with body tissues and can bond with adjacent bones during healing.
In recent years, implants made from Zirconia, which is white rather than metallic in color, have bone-bonding qualities similar to those of Titanium, which has become popular and has been shown to be as effective as titanium implants.
Benefits Of Choosing Dental Implants
There are various benefits of choosing dental implants if you have missing or lost teeth.
- Preserves your facial structure
- Protects healthy teeth
- Restore your smile
- Long-lasting solution
- You can eat anything you want
- Improves your speech
- Boosts self-esteem
- Stable and comfortable
-
Bridges
A dental bridge consists of false teeth and crowns that cover natural teeth. As the name implies, it bridges the gap between the teeth by replacing missing teeth and restoring chewing function.
This helps improve overall oral health and enhance appearance. Many dental insurance plans cover the bridge’s cost, and many are now covering implants as well.
A dental bridge may needed to be replaced every 5 to 10 years, depending on its care, while implants are a permanent solution for missing teeth.
There are certain factors that can reduce the life span of bridges, including implants, such as dental hygiene and oral care.
Things To Remember While Choosing Bridges
The supported bridge does not stimulate the natural growth of the bone beneath it, which causes the bone to deteriorate over time.
Bridges generally fail after 5 -10 years because they are difficult to floss, which makes the root below and around the bridge highly susceptible to tooth decay.
-
Partial Dentures
It is a plate with one or more false teeth, which may be made of plastic or a mix of plastic and metal. Both types may have clips to keep the denture in your mouth in place.
Depending on where they are, some of the denture clips may show when you smile or open your mouth.
They are a set of removable false teeth that are made up of acrylic (plastic), nylon, or metal. They perfectly fit over the gums to replace missing teeth and eliminate a variety of potential problems caused by gaps.
Dentures may help to prevent problems with eating and speaking. If you need a complete denture, it can enhance your appearance, giving you symmetrical teeth and a perfect smile that boosts confidence.
Things To Remember While Choosing Dentures
Partial dentures are not as stable and comfortable as dental implants, and they can affect your eating and speech. This restoration is less expensive but doesn’t look as natural or function like dental implants.
The bone beneath a removable denture may deteriorate over some time, changing the appearance of your smile and face.
Key Takeaways
Dental implants, bridges, and dentures are three options for replacing a missing tooth. Bridges are more likely to be covered by your insurance company at a lower cost than others.
But, if cost and time are not an issue for you and your overall health is good, then dental implants may be the best option for you.
However, a dentist or a dental professional may be able to advise you on the best dental treatment by examining your oral and health conditions.
‘Dacula Dental’ understands the importance of having a perfect smile, and we strive to ensure your dental and overall oral well-being.
Our friendly atmosphere is crafted to provide comfort and relaxation for each of our patients. Our dental professionals are committed to assist you in obtaining and preserving a vibrant and a healthier smile.
The Road To A Confident Smile Starts Here
FAQs
1. What are dental implants and how do they work?
Dental implants are artificial tooth roots, usually made of titanium, that are surgically placed into the jawbone. Over time, the bone fuses with the implant in a process called osseointegration, creating a strong foundation for a crown, bridge, or denture.
2. How long do dental implants last?
With proper care, dental implants can last 20 years or more. Many last a lifetime. Good oral hygiene, regular dental checkups, and avoiding tobacco are key factors in maximizing their lifespan.
3. Are dental implants painful?
Most patients report minimal discomfort during and after the implant procedure. Local anesthesia is used, and post-surgery pain is usually managed with over-the-counter medication. Many say it’s less painful than a tooth extraction.
4. How much do dental implants cost?
Dental implant costs vary, but in the U.S., a single implant typically ranges from $3,000 to $5,000. This includes the implant post, abutment, and crown. Full-mouth restorations can be significantly higher depending on complexity.
5. How long does it take to get a dental implant?
The full process can take 3 to 6 months or longer. It includes the initial consultation, implant placement, healing period for bone integration, and finally attaching the crown. Immediate-load implants may shorten the timeline in certain cases.
6. Who is a good candidate for dental implants?
Ideal candidates have healthy gums, sufficient jawbone, and are in good overall health. If you’ve lost teeth due to decay, injury, or gum disease, implants may be an excellent option especially if you’re not comfortable with dentures or bridges.
7. What are the advantages of dental implants over dentures?
Implants are more stable, feel like natural teeth, and don’t slip while talking or eating. They also help preserve jawbone density, which dentures can’t do. Many patients find them more comfortable and confidence-boosting in the long term.
8. Do dental implants look natural?
Yes. Modern dental implants are custom-designed to match the color, shape, and size of your natural teeth. Most people can’t tell the difference between an implant and a real tooth.
9. What is the recovery time after dental implant surgery?
Initial recovery from the implant surgery takes about 1 to 2 weeks. However, full osseointegration (when the implant fuses with the bone) can take several months before the permanent crown is placed.
10. Are there any risks or complications with dental implants?
Like any surgery, dental implants carry some risks such as infection, nerve damage, or implant failure. However, these are rare, especially when the procedure is performed by a skilled dentist or oral surgeon.
Referral Site –
Oral health Foundation [Bridges and partial dentures]
You may be wondering about the most effective ways to clean your teeth. Should you use a manual or electric toothbrush? Soft or firm bristles?
Achieving healthy teeth takes a lifetime of care. Even if you have good and healthy teeth, and get compliments about having nice teeth, it’s crucial to take the right steps to take care of them to prevent teeth and gums problems, and have a shiny and bright smile.
It involves getting the right oral care and being mindful of your daily habits. Dental hygiene is necessary to maintain healthy teeth and gums. Without caring and maintaining proper hygiene and dental care, comes various complications that lead to pain, speech problems, and decreased confidence.
Benefits of Regular Teeth Cleaning
Regular professional teeth cleaning is crucial not just for a sparkling smile but for your overall health. Here’s why you shouldn’t skip your next appointment:
Prevents Cavities and Gum Disease
Over time, plaque naturally builds up on teeth. If not removed, it hardens into tartar, leading to cavities and periodontal disease. Routine cleanings eliminate this buildup, keeping your teeth and gums healthy.
Freshens Breath and Enhances Smile Appearance
Persistent bad breath (halitosis) often stems from poor oral hygiene. A dental cleaning removes odor-causing bacteria, leaving your breath fresher and your smile noticeably brighter. Polishing also removes surface stains caused by coffee, tea, and smoking.
How Often Should You Get Your Teeth Cleaned?
A common question is: how often should you get your teeth cleaned?
General Recommendation: Every 6 months for most people.
Special Cases: If you smoke, have gum disease, diabetes, or a history of cavities, your dentist may recommend cleanings every 3–4 months.
Frequent cleanings lower your risk of more serious dental issues and save you money in the long term.
Cost of Teeth Cleaning: What to Expect
When searching for “teeth cleaning near me cost,” you’ll notice it varies:
Without Insurance: Expect to pay between $75 and $200 depending on your location and the dental office.
With Insurance: Many dental plans fully cover preventive cleanings twice a year.
Additional Costs: If you need deep cleaning (scaling and root planing), it can cost more, ranging from $300 to $900.
9 Best Ways to Keep Your Teeth Clean And Healthy
If you are wondering how to have healthy teeth and gums, then you must remember to use these teeth care tips at home to have shiny and healthy teeth for a brighter smile.
Here are some of the best ways how to keep your teeth clean and healthy –
1. Brush Your Teeth Regularly
- Your everyday hygiene habits are crucial to your overall dental health, you must brush your teeth for about 2 minutes before going to bed every day.
- Your dentist may give you more advice based on your dental health and needs on how many times you should brush.
- This is the best way to keep your teeth clean, and the way you brush is equally important, in fact, poorly brushing your teeth is almost similar to not brushing at all.
- Take your time, moving the toothbrush gently on your teeth in circular motions to remove plaque because it can harden, leading to calculus buildup and gingivitis (early gum disease).
- Make sure to clean all the surfaces and the chewing surfaces of your teeth, which should take about 2 minutes.
2. Choose the Best Toothpaste
- There are different brushes in the market, ranging from soft to hard to electric. The best kind is the softer ones, as our teeth do not require hard brushing.
- For most adults, a toothbrush with a small head, and round bristles is good.
- If you’re using an electric brush with an oscillating or rotating head, it may work better than a manual toothbrush.
- Making sure to thoroughly brush your teeth at least two times a day is more important than the type of brush you choose to brush with. If in doubt, ask your dentist.
3. Floss Regularly While Brushing
Flossing isn’t done just for dislodging food wedged between your teeth.
Regular flossing also reduces gum disease and prevents bad breath by removing plaque.
It’s best to floss before brushing your teeth.
- Take 30 cm to 45 cm of floss or dental tape and take it so you have 3cm or 4cm of floss left between your hands.
- Slip it between the teeth and into the areas between your teeth and gums, as far as it will go well.
- Floss your teeth with 8 to 10 strokes, up and down in a circular motion between each tooth, to remove food and plaque.
4. Clean Your Tongue
- Are you confused about where the bad breath comes from?
- It’s probably your unclean tongue, and it doesn’t matter how talkative you are, you must clean your teeth regularly to have a clean and fresh breath.
- Plaque occurs not only on the teeth and crevices but also on the tongue.
- Over time, it can cause a major foul breath if you do not brush correctly.
5. Use mouthwash To Maintain Dental Hygiene
Advertisements make mouthwash seem like it is necessary for oral health, but many people skip it because they don’t know how it works.
Using a mouthwash containing fluoride can help to prevent tooth decay, but avoid using mouthwash (with fluoride) immediately after brushing your teeth otherwise it’ll wash the concentrated fluoride present in the toothpaste that is left on your teeth.
Choose a different time to use mouthwash probably after lunch.
Don’t eat or drink anything for 30 minutes after using a fluoride mouthwash.
6. Watch What You Eat To Maintain Your Oral Hygiene
Your diet and the type of intake you take impact your oral hygiene and help you keep your teeth healthy.
Make sure to have a balanced diet that contains plenty of vegetables fruits, and proteins, but limit your food intake that are rich in fat and sugar.
7. Watch What You Drink Too
Sugar converts into acid in the mouth later, which can erode the enamel of teeth. These acids are what lead to cavities. Sugary drinks can harm your teeth. Beverages that are rich in sugar can cause tooth decay.
Water is considered to be the best drink for your overall health including oral health. Doctors also recommend drinking water after every meal. This helps wash out some of the negative effects caused by sticky and acidic foods and drinks in between brushes.
So try to avoid the overly processed stuff, stop cutting food into tiny pieces, and get those jaws working!”
8. Stay Away From Cigarettes And Coloured Foods
Smoking also affects your dental hygiene leading to gum disease and bacteria on the teeth getting under the gum which leads to increased levels of plaque if the germs get to stay on the teeth for longer.
Just like smoking, colored foods also impact the color of your teeth, making them look yellowish and feel unhealthy and unrefreshed.
9. See Your Dentist At Least Twice A Year
Even the most dutiful flossers and brushes consult a doctor for oral care. You should see your dentist for cleaning and checkups from time to time, and at least twice a year.
Not only will a dentist remove calculus and look for cavities, but they will also spot the potential cause of other upcoming issues, and offer treatment solutions to prevent and stop any dental problems.
Key Takeaways
Caring for your teeth and doing oral care is part of daily life, but people neglect or forget about their oral health due to busy schedules and unhealthy eating habits.
But, now that you are aware of these issues and know the best way to keep your teeth clean and healthy, and how to have healthy teeth and gums, it’s time to see a dentist and start caring for your oral and dental health before it’s too late.
FAQs
1. How long does a teeth cleaning take?
A typical professional teeth cleaning session lasts between 30 to 60 minutes, depending on plaque buildup and your overall oral health.
2. Is teeth cleaning painful?
Teeth cleaning is usually painless. Some people may experience mild sensitivity or discomfort during scaling if there’s heavy tartar buildup or gum inflammation, but numbing options are available if needed.
3. What should you not do after a teeth cleaning?
After a cleaning, avoid consuming staining foods or drinks like coffee, tea, wine, and berries for at least a few hours. Also, be gentle with flossing if your gums feel sensitive.
4. Can teeth cleaning remove stains?
Yes, professional cleanings can effectively remove many surface stains caused by coffee, tea, wine, and tobacco use, making your smile look noticeably brighter.
5. What happens if you don’t get your teeth cleaned?
Skipping regular cleanings can lead to plaque hardening into tartar, causing cavities, gum disease, bad breath, and even tooth loss over time. Plus, untreated oral infections can affect overall health, including heart disease risks.
For most kids, holidays mean lots of junk food and candy. While we want our children to enjoy the holiday season, we also want to keep their teeth healthy. Here are a few tips from Colgate to help maintain your children’s oral health despite increased sugar intake.
Cavities are common in childhood, but they can be prevented with regular brushing and flossing. The type of food you offer your children also plays a vital role in their oral health, which directly impacts their overall well-being.
7 Child Dental Care Tips For Healthy Teeth And Gums
Our teeth help us eat, talk, and smile, which is a regular activity in a person’s life. Teach your child good dental habits for a brighter and shinier smile.
During holidays, kids do not want to eat homemade food. Instead, they binge eat unhealthy and processed food that is good in taste but affects their oral health, leading to cavities, tooth decay, and toothache.
Regular teeth cleaning habits are essential for maintaining a child’s oral health. Follow these child dental care tips and help to make your kid’s teeth healthy and decay-free.
Brush Your Kids Teeth Twice A Day With Fluoride Toothpaste
Start with cleaning your kid’s teeth even if all of their teeth are not fully developed or if they are under 1 year of age. Take a clean cloth and clean their teeth and gums.
Use a small and soft bristles brush, and clean their mouth thoroughly with water at least 2 times a day.
But if your child is one year old, then you must regularly brush their teeth at least 2 times a day. First when they wake up and second at night before going to bed.
Use Pea-Sized Amount Of Toothpaste
The type and amount of toothpaste that you use for your kid also matters the most.
Dentists recommend taking a small, pea-sized amount of fluoride toothpaste for kids 3 – 6 years of age.
And make sure they do not swallow toothpaste. Excessive toothpaste (including fluoride) intake can lead to fluorosis, a cosmetic defect in tooth enamel.
Help Your Child Brush Their Teeth Properly
You must help and teach your child how to brush their teeth properly. Soft brush their teeth with a small toothbrush that is soft and avoid using hard bristles that can damage their gums.
Show your child the correct way to brush their teeth, and gently use the brush in circular motions, brushing all sides of each tooth.
Pay extra attention to the back of the teeth where cavities usually form, and brush for at least two minutes.
Limit Sugary Drinks And Foods
Avoid binge eating on sugary drinks and food. Sugar consumption in excess is a major contributor to kids’ teeth cavity and tooth decay. Encourage healthy habits by limiting sugary foods and drinks.
Avoid offering sugary snacks and drinks; instead, opt for healthy snack options like fruits, whole-grain alternatives, and homemade foods.
Encourage your Child To Have Fruits And Vegetables
Encourage your child to have more fruits and vegetables whenever they feel hungry, and do not give highly processed or unhealthy foods like pizza, burgers, soft drinks, and chocolates.
Snacking on unhealthy food leads to cavities and toothache in early childhood, which disturbs a child’s daily activities.
Give Them Protein And Calcium Rich Foods
Give them calcium-rich diets containing yogurt, broccoli, and milk, as well as protein-rich foods like lean meats (Turkey), chicken, and white fish, which are a good source of protein.
Having a calcium and protein-rich diet helps to make kids’ teeth stronger and shinier.
Take Your Child To The Dentist For Regular Checkups
According to the American Academy Of Pediatric Dentistry (AAPD), every parent should take their child to the dentist by their first birthday or when their first tooth appears, which comes first.
The dentist may examine the teeth, gums, jaw, bite, and oral tissues, he may clean the teeth, plaque or stains on the teeth. The dentist may show you or teach your child how to clean their teeth daily.
Top 4 Child Dental Care Benefits
Good oral hygiene with these child dental care tips helps in developing healthier teeth and prevents tooth decay and gum disease. Here are the Top 5 child dental care benefits that impact your child’s overall health –
Prevents Tooth decay
Healthy oral care habits and dental checkups can help a child avoid tooth decay and the pain that comes with it. A dentist will identify tooth decay through oral examination and X-rays.
The timely treatment and recovery of cavities typically ensures less invasive treatments, which prevents the need for filling or extractions.
Avoid Kids Teeth Cavity
Cavities are one of the most common oral problems in children and toddlers, and they can develop in your child’s primary teeth.
Regular oral care and brushing can prevent kids’ teeth cavity that can be painful, causing discomfort.
Gum disease
It is also known as periodontal disease, which is usually caused by plaque formation, a sticky layer (bacteria) that forms on the teeth and gums. This usually happens when a child avoids or does not properly brush their teeth on a regular basis.
Improved self-esteem
Having healthy gum and white teeth helps you smile brighter without hesitation, which improves a child’s self-esteem and boosts confidence.
Key Takeaways
Keeping your child’s teeth healthy is not a complicated task, with just a little guidance and best child dental care tips, you can teach them healthy habits that can help them have a lifetime of smile.
Encourage them to have a healthy diet, including fruits and vegetables, and make water their go-to drink for your kid’s teeth health.
By following these simple ways to keep your teeth healthy, you can ensure your child’s teeth stay strong and beautiful for years to come. And if you want to get expert advice from the best pediatric dentists, Dacula Dental is here to help.
We have a team of experienced and professional dentists who can help you treat your kids with the utmost care and expertise. Book an appointment now to know more.
A Healthier And A Brighter Smile Awaits You