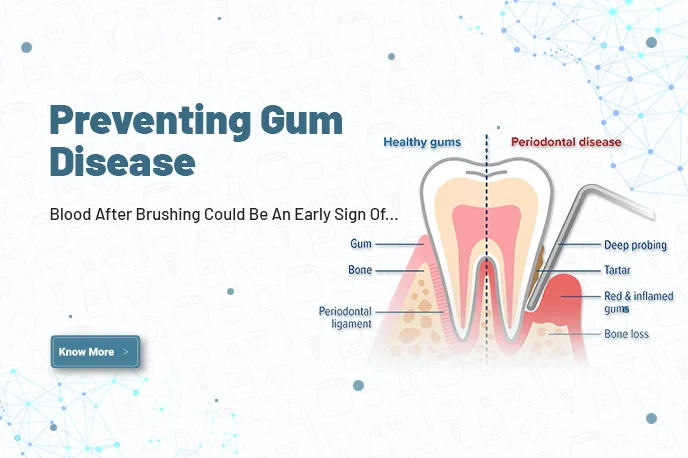
Keeping your teeth clean and cavity-free doesn’t mean you have healthy gums, either. Since it’s painless, you may not even know whether there are any problems with your gums.
Severe Gum infection affects around 19% of the adult population, with more than one billion cases worldwide. According to American Dental Association (ADA), gum diseases like Gingivitis and Periodontitis are the major causes of tooth loss in adults.
Types Of Gum Diseases
There are generally four types of gum diseases that can affect overall oral health and cause discomfort while eating and speaking.
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is a gum disease that is considered to most commonly cause inflammation of gums, which is found in over 50% of adult U.S. population. Early signs of gum disease (Gingivitis) are bleeding, swelling, and redness in the gums.
Periodontitis
Periodontitis exhibits signs similar to Gingivitis, except for loss of tissue and jawbone. The damage of periodontitis is particularly concerning because the loss of gum tissue and bone cannot be recovered.
Untreated Periodontitis results in teeth loss, and it can sometimes increase the risk of stroke, heart attack, and other health problems.
Periodontitis is caused due to bacterial infection that affects gums and tissues. It is a chronic Periodontal disease that is triggered by bacterial microorganisms and involves severe chronic inflammation, leading to the destruction of the teeth’ supporting apparatus.
Gum Recession
Gum recession is a common adult gum problem in which the root of the tooth is exposed, and the gum line pulls away from its original place. This could be a result of gum disease, as the jawbone that surrounds the teeth is lost.
Gum Abscess
Another gum problem is gum abscess, also known as periodontal abscess. It causes symptoms like a blister or a bump in the gum containing pus. It is caused by a bacterial infection in the deep gum, causing pain and swelling.
Oral Cancer
A less common periodontal disease is oral cancer, which can occur in all soft tissues within the mouth. It may appear as a red or white patch or a sore on the gums that does not heal.
Causes Of Periodontal Diseases
Gum inflammation or periodontal disease is primarily caused by plaque formation, a sticky layer of bacteria on the teeth and gums that leads to infection.
Plaque – It forms when bacteria in the mouth feed on sugars and starches from food particles, creating a sticky film on the teeth.
Tartar – Plaque that isn’t removed through regular brushing and flossing hardens and becomes tartar, which is a harder substance that can be removed by a dentist.
Irritation – Plaque and tartar irritate the gum tissues, causing gum inflammation and infection that can lead to Pyorrhea.
Dental Treatments For Serious Gum Disease
Periodontal treatment depends on your dental health and the stage of the serious gum disease.
Neurological Treatments –
-
Professional Dental Cleaning
During your dental checkup, a dentist will remove the tartar from your teeth, which can only be removed through professional dental cleaning.
If you have Gingival disease symptoms, you may be recommended for professional dental cleaning more than twice a year. It is not a treatment, but it is a preventative measure for Periodontal disease.
-
Scaling And Root Planing
It is a process of deep cleaning done under a local anesthetic in which plaque and tartar are scraped away (scaling) from the surface of your teeth and gums, which hardens and leads to Periodontal disease.
The rough surfaces of the teeth are made smooth (planing). It provides a clean surface on the teeth that allows your gums to reattach.
Surgical Treatments –
Your dentist may recommend you undergo Gingival disease surgery if the tissues around your teeth can’t be repaired and neurological treatment is not enough for your oral condition.
-
Flap Surgery
During this treatment, your gums are lifted back to remove tartar, and the irregular surfaces of the bone are smoothed out to limit areas where bacteria usually hide. Your gums are then placed to fit around your tooth, which reduces the space between your gum and tooth.
-
Bone Grafting
In this procedure, dentists use fragments of your own bones, synthetic or donated bones, to replace them with damaged teeth bones due to Gingival disease. Bone grafts serve as a platform for the regrowth of bone, which ensures stability to your teeth.
-
Soft Tissue Grafts
It reinforces thin gums and fills the gaps where your gums have receded due to Gingival disease. Grafted tissue is most often taken from the roof of your mouth and stitched into place to add tissue to your affected area.
-
Bone Surgery
In this process, a dentist smoothest out shallow craters in your bone caused due to bone loss. After surgery, the bone around your tooth is reshaped to prevent bacteria from collecting and growing on your teeth.
What Are The Common Risk Factors For Periodontal Problems
Some of the most common risk factors contributing to periodontal diseases are –
Poor Oral Hygiene
Neglecting proper cleaning of teeth and tongue and not flossing regularly allows plaque and tartar to accumulate, which increases the risk of Periodontal disease.
Smoking
Regular smoking weakens a person’s immune system and reduces the ability to fight against infections, putting individuals at higher risk of Gingival disease.
Systemic Diseases
Certain medical conditions, especially diabetes, can increase the risk of gum disease. Using certain medications can cause dry mouth, which increases the risk of Gingival disease.
Diet
Diets that are rich in sugar and high in carbohydrates can contribute to plaque formation, which can lead to Gum infection.
Keys To Preventing Gum Disease
In order to preventing gum disease, you must follow these things regularly –
- Brush your teeth twice a day
- Floss regularly
- Don’t forget to clean your tongue
- Use an antibacterial mouthwash
- Replace your toothbrush regularly
- Regular checkups and cleanings
FAQs
Q1. How do I know if I’m getting gum disease?
A: If your gums are looking red, swollen, bleeding when you brush, or you’re dealing with nonstop bad breath, those are big red flags. These are early signs your gums need some serious love — and fast. Catch it early, and you can usually fix it before it gets serious.
Q2. What’s the deal with treating serious gum disease?
A: If things get bad (like with Periodontitis), your dentist might need to do deep cleanings like scaling and root planing. For even more serious cases, surgeries like flap surgery, bone grafts, or gum grafts can help save your teeth and rebuild what’s been lost.
Q3. What makes gum disease worse over time?
A: Skipping brushing, barely flossing, smoking, eating tons of sugar, and not treating early signs all make gum disease go from “no big deal” to “serious problem” pretty fast. Chronic illnesses like diabetes can also crank up your risk.
Q4. Can I fix gum disease naturally at home?
A: You can totally turn around early gum disease (like Gingivitis) by stepping up your brushing, flossing, and using mouthwash. But if it’s already advanced (like full-blown Periodontitis), you’re going to need a dentist’s help no amount of DIY can reverse bone loss.
Q5. What’s the best way to avoid gum disease for good?
A: Make brushing and flossing part of your daily non-negotiables, clean your tongue (seriously, it matters), ditch smoking, eat more whole foods, swap sugary snacks for healthier options, and get pro dental cleanings twice a year. Your gums will thank you — for life.
Final Thoughts
Most gum problems are preventable and can be controlled if the early signs of gum disease are addressed. For individuals with genetic gum disease, it can be a lifelong effort to preventing gum disease, and to keep the condition in check.
The Secret To A Winning Smile Is Oral Care
Referral Site –
[CDC] February 24, 2025 Smoking, Gum Disease, and Tooth Loss
Smoking harms your teeth and significantly affects your overall oral health. According to research done by (the Academy Of General Dentistry), it is found that smoking a pack of cigarettes daily can lead to losing around two teeth every decade.
Tobacco and nicotine are significant culprits for severe factors contributing to teeth discoloration. Smoking and chewing tobacco and nicotine leads to damaging the tooth enamel.
Most people are aware that smoking is harmful to their health. It can cause many different severe medical problems and, in some cases, fatal oral diseases. However, many people do not realize the damage until it’s too late.
How Does Smoking Harms Your Teeth, Gums, And Oral Health
People who smoke heavily have a higher risk of gum problems, tooth decay, complications after tooth removal and dental surgery in the mouth, and an increased risk of mouth cancer.
Smokers are more likely to get infections and don’t heal as well as non-smokers. Those who smoke daily can have serious oral problems. Certain circumstances are mild, but some of them can be highly alarming.
Some Of the most common oral problems affecting people who smoke are –
- Gum or periodontal disease
- Tooth decay
- Tooth loss
- Mouth cancer
- Decreased taste
- Bad taste and causes bad breath (Halitosis)
- Poor healing after tooth removal
- Slow healing after dental gum or oral surgery
Gum Disease and Tooth Loss
Smoking potentially increases the risk of periodontal diseases and by accelerating tooth loss. According to an article, a Birmingham University study indicated that male smokers face a 3.6 times higher likelihood of tooth loss as compared to non-smokers.
In contrast, female smokers face only 2.5 times increased risk of tooth loss.
The risk of gum disease is higher –
- If you are a person who smokes at least 10 cigarettes in a day, as compared to someone who doesn’t smoke.
- The risk increases more likely in those who smoke 4 – 5 times more heavily.
- The longer you smoke, the higher your risk of developing gum disease.
- Gum disease treatments may not succeed for people who smoke.
- Tobacco use in any form, such as cigarettes, pipes, and smokeless (spit) tobacco, can raise the risk for gum disease.
Risk Of Oral Cancer
Smoking harms your teeth by increasing the risk of causing oral cancer. The Oral Health reports that those who smoke are ten times more likely to have mouth cancer than non-smokers.
Smoking weakens the immune system, slowing down or stopping the healing process after dental treatments or surgery.
According to World Health Organization (WHO), smokers’ teeth take a relatively longer time to recover after dental surgery due to compromised immune responses.
Symptoms Of Mouth Cancer –
- Persistent ulcers in the mouth that do not go away after 7 – 10 days and are particularly not painful.
- Red or white patches in the mouth
- Swelling in the mouth
- Your dentures will not fit properly
Risk Of Tooth Decay
Tobacco use and smoking harms your teeth and gums. Smoking and using tobacco products can cause cavities on the surface of the teeth, which leads to tooth decay over time. Your teeth may even break down, which can be painful and require costly treatments.
Discoloration and Staining on teeth
The chemicals found in tobacco products like cigarettes and cigars can cause discoloration and stains on teeth. When you smoke, the nicotine and tar in tobacco can settle within the tooth enamel.
This can turn your teeth yellow very quickly. If you’re a heavy smoker, your teeth could eventually turn brown.
Tobacco stains are often tough to remove but can usually be treated using professional stain removal and teeth whitening treatment carried out or prescribed by your dentist.
Impaired Healing
Smoking and tobacco use make it harder for your immune system to fight against infection, which aids in slowing down your healing process after tooth recovery, injuries in the mouth, and any other dental treatments.
Smoking and tobacco use over time can lead to –
- Dry socket – slow healing and painful tooth socket after tooth removal.
- Increased pain after oral and gum surgery
- Your dental implant surgery will not be successful if you smoke.
Does Smoking Causes Bad Breath
In research, it is found that there is a consistently strong association between smoking and increased risk of halitosis. Cigarette smoke contains many ingredients that can lower the oxygen level and antibiotic effects.
It contributes to dry mouth, gum disease, and tooth decay, which contribute to bacterial growth that causes dry mouth or halitosis.
Chemical compounds present in cigarette smoke can also contribute to mouth odor, which is popularly referred to as a smoker’s breath.
Smoking can cause dry mouth due to periodontal diseases, hyposalivation, and dental caries.
Smoking and using tobacco also causes a significant imbalance in the oral microbiome that causes bad breath or halitosis.
Ways To Combat Bad Breath Caused Due To Smoking
Bad breath is caused by reduced saliva production during the early stages of gum disease or dry mouth. Here are certain effective ways you can combat bad breath caused by smoking.
- Brush your teeth twice a day
- Floss regularly at least once
- Increase fluid intake to prevent your mouth from getting dry
- Use antibacterial mouthwash
- Use Fluoride based toothpaste
- Use peppermint or chew sugarless gums
- Schedule a regular dental cleaning to remove plaque and tartar from your teeth.
Key Takeaways
Quitting smoking helps to improve mouth cancer, and it also reduces the potential risk of gum diseases and enhances the person’s response to gum treatment. Avoid smoking if you want to keep your teeth and gums clean and healthy.
If you’re not ready to quit, you can still care for your teeth. The same dental health habits apply: Brush at least twice a day and floss daily. See your dentist at least twice yearly to help fight against gum disease and prevent tooth stains.
Say No to Smoke, Say Yes to a Healthy Smile
Everyone knows that smoking causes lung cancer. Even most smokers are aware of this risk when they light up. But another danger of smoking that gets less attention is the damage it does to your teeth. Smoking breeds bacteria, which causes bad breath, yellow teeth, and gum disease. Every smoker knows …
FAQs
Q 1 : How does smoking affect your gums?
A: Smoking restricts blood flow to the gums, reducing the oxygen and nutrients they need to stay healthy. This can lead to gum inflammation, slower healing, and a higher risk of infections like gingivitis and periodontitis.
Q 2 : What are the effects of smoking on the mouth?
A: Smoking damages nearly every part of the mouth, including the gums, teeth, tongue, and inner cheeks. It causes bad breath, stains teeth, reduces saliva flow, and significantly increases the risk of oral cancers.
Q 3 : Can smoking cause gum disease?
A: Yes. Smoking is a major risk factor for gum disease. It weakens the immune system, making it harder to fight off a gum infection, and reduces the effectiveness of treatment once gum disease sets in.
Q 4 : Why is gum disease worse in smokers?
A: In smokers, gum disease progresses more rapidly and often silently because smoking masks common symptoms like bleeding gums. The decreased blood flow and immune response in the gums make the condition harder to detect and treat.
Q 5 : What visible signs appear in the mouth from smoking?
A: Visible signs include yellow or brown teeth, receding gums, dry mouth, white patches (leukoplakia), and in advanced cases, oral lesions or ulcers that may indicate oral cancer.
Q 6 : How does smoking damage your teeth?
A: Smoking stains teeth, promotes plaque and tartar buildup, leads to enamel erosion, and increases the risk of cavities and tooth loss. It also contributes to chronic bad breath.
Q 7 : Can smokers get dental implants successfully?
A: Smokers can get dental implants, but their risk of implant failure is higher. Smoking impairs healing and bone integration, increasing the likelihood of infection and complications. Quitting or reducing smoking significantly improves outcomes.
Q 8 : How does smoking affect overall oral health?
A: Smoking impacts all aspects of oral health, including increasing risks for gum disease, tooth loss, oral cancer, delayed healing after dental procedures, and poorer outcomes in general dental care.
Q 9 : Is there a direct link between smoking and periodontal disease?
A: Yes. Smoking is one of the strongest predictors of periodontal (gum) disease. It makes the gums more vulnerable to bacterial infections and hinders the healing process, worsening the severity and progression of the disease.
Q 10 : Why is smoking considered harmful to dental health?
A: Smoking harms dental health by weakening the structures that support teeth, staining enamel, suppressing immune response, and increasing the risk for both periodontal disease and oral cancer.
Q 11: What steps can smokers take to protect their dental health?
A: Smokers should maintain strict oral hygiene, visit their dentist regularly, use antimicrobial mouthwash, avoid tobacco use when possible, and consider cessation programs to reduce long-term damage.
Your child’s first trip to the dentist is an exciting experience for your child. But it can also be a source of anxiety for both parent and child. Setting a positive tone before the first dental visit can heal and ensure that your child feels comfortable during the dental procedure.
Early dental care is crucial for parents to establish oral care routines and healthy oral hygiene habits. Starting dental visits at the age of one or as soon as your child’s first tooth emerges is important to identify any potential issues.
If you are preparing for your child’s first visit to the pediatric dentist, then here are five tips to make your child’s experience exciting and enjoyable.
-
Start Dental Visits Early
According to American Academy Of Pediatric Dentistry (AAPD), every parent should take their child to the dentist by their first birthday or when their first tooth appears, which comes first.
Pediatric Dentistry focuses on early prevention, which is crucial for setting a strong foundation for oral health. Early visits to a dentist help your child become familiar with the dentist’s office, which reduces fear and anxiety in future dental visits.
The earlier you educate your child about dental care, the better it is to ensure their oral health. A visit to a Pediatric Dentist at an early stage ensures that any potential issues are identified and addressed early on.
-
Choose A Pediatric Dentist
Visiting a pediatric dentist who specializes in children’s dental care has numerous benefits. A pediatric dentist (dentist for kids) has specialized training in addressing oral issues, especially in newborns, adolescents, and teenagers.
They have a creative, child-friendly atmosphere in their office equipped with toys, colorful decor, and gentle approaches to alleviate anxiety and discomfort in children. They teach and educate children about oral hygiene and how children can take care of their teeth.
Pediatric dentists use specialized techniques to make sure your child feels comfortable and safe during dental procedures.
-
Prepare Your Child For a Dental Visit
Preparing your child for first dental visit is crucial to easing any doubts and anxiety in children. Talk positively and explain what will happen during the visit, ensuring that the dentist is there to help them keep their teeth strong.
Reading children’s books and role-playing at home can make your child familiar with the process.
Determine any concerns that your child has and make them feel more confident about their upcoming appointment.
-
Be Supportive
Offer continuous assurance and positive reinforcement to make your child comfortable and stress-free before going to a dentist’s office.
Encourage them to be confident and cooperative during dental procedures or procedures. Praise your children’s efforts and emphasize the importance of oral health.
Stay calm, composed, and happy to help reassure your child that the dental visit is just a normal part of daily life.
Your supportive nature can significantly influence your child’s experience, making them feel comfortable and secure during their time at the dentist.
-
Celebrate And Reward Your Child
Celebrate and reward your children with their favorite gifts for a successful dental visit with positive encouragement.
Appreciate their bravery and good behavior during the dental process and praise their efforts in taking good care of their oral health.
Celebrating first dental visit of your child helps to boost confidence and fosters a positive outlook on future dental visits, making them less anxious and more enjoyable for your child.
How Important Is Your Children’s Dental Care
From brushing your child’s teeth to their first trip to the dentist, here are some of the common tips on how you can take care of your children’s dental care.
Cavities are common in childhood. However, they can be prevented by regular brushing and cleaning of teeth. Ensuring your children’s dental care plays a vital role in their oral health, which impacts their overall health.
-
Help Your Child Brush Their Teeth Properly
You must help and teach your child how to brush their teeth properly. Soft brush their teeth with a small toothbrush that is soft and avoid using hard bristles that can damage their gums.
Show your child the correct way to brush their teeth, and gently use the brush in circular motions, brushing all sides of each tooth.
Pay extra attention to the back of the teeth where cavities usually form, and brush for at least two minutes.
-
Limit Sugary Drinks And Foods
Avoid binge eating on sugary drinks and food. Sugar consumption in excess is a major contributor to kids’ teeth cavities and tooth decay. Encourage healthy habits by limiting sugary foods and drinks.
Avoid offering sugary snacks and drinks; instead, opt for healthy snack options like fruits, whole-grain alternatives, and homemade foods.
-
Encourage your Child To Have Fruits And Vegetables
Encourage your child to have more fruits and vegetables whenever they feel hungry, and do not give highly processed or unhealthy foods like pizza, burgers, soft drinks, and chocolates.
Snacking on unhealthy food leads to cavities and toothache in early childhood, which disturbs a child’s daily activities.
-
Give Them Protein And Calcium Rich Foods
Give them calcium-rich diets containing yogurt, broccoli, and milk, as well as protein-rich foods like lean meats (Turkey), chicken, and white fish, which are a good source of protein.
Having a calcium and protein-rich diet helps to make kids’ teeth stronger and shinier.
Key Takeaways
Managing your children’s dental care is not a complicated task, with just a little guidance and best child dental care tips, you can teach them healthy habits that can help them have a lifetime of smile.
Encourage them to have a healthy diet, including fruits and vegetables, and make water their go-to drink for your kid’s teeth health.
By following these simple ways to keep your teeth healthy, you can ensure your child’s teeth stay strong and beautiful for years to come. And if you want to get expert advice from the best pediatric dentists (dentists for kids), Dacula Dental is here to help.
Give Your Kids the Gift of a Healthy Smile!
FAQs
Q1. When should I schedule my child’s first dental visit?
A: According to the AAPD, schedule your child’s first dental visit by their first birthday or when the first tooth appears whichever comes first.
Q2. How do I prepare my child for their first dental visit?
A: Use positive language, role-play dental visits at home, read books about going to the dentist, and answer all their questions calmly and confidently.
Q3. Why should I choose a pediatric dentist instead of a general dentist?
A: Pediatric dentists have specialized training to care for children’s oral health and create a child-friendly environment that helps reduce fear and anxiety.
Q4. How often should children see the dentist?
A: Children should visit the dentist every six months for regular cleanings and checkups unless otherwise recommended by their pediatric dentist.
Q5. What if my child is afraid of the dentist?
A: Stay supportive and patient. Gradual exposure, positive reinforcement, and a compassionate pediatric dentist can help your child overcome dental anxiety over time.